If Nations Trade on the Basis of Comparative Advantage:
Dall trading partners can gain from trade. Opportunity cost of making that good for Country A is lower than Country B regardless of absolute figures.

Comparative Advantage And The Gains From Trade Article Khan Academy
Absolute advantage and comparative advantage are two important concepts in economics and international trade.

. The Comparative Advantage Theory suggests that countries who have a lower opportunity cost giving up production of a particular good at producing a certain good should efficiently allocate their resources to producing just that good so after domestic consumption. If you look at the pattern of trade it seems to be between similarswealthy nations trade with each other. Ricardo has demonstrated that absolute cost advantage is not a necessary condition for two countries to gain from trade.
Bexporting nations gain from trade and importing nations lose. I have recently covered the theory of Comparative Advantage within International Trade. If country A produces can produce 20 Bananas or 40 Tyres and country B produces 10 Bananas or 30 Tyres.
48The introduction ofa tariff will be expected to reduce imports. D all trading partners mutually gain. Aa nation usually can gain from trade only at the expense of its trading partners.
The theory states that if countries specialize in and export the goods that they have an absolute advantage which can be produced with fewer resources then they allocate more resources and increase production and consumption. To him comparative difference in cost is a sufficient condition for trade to emerge. In an economic model agents have a comparative advantage over others in producing a particular good if they can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price ie.
Comparative advantage describes the economic reality of the work gains from trade for individuals firms or nations which arise. Cimporting nations gain from trade and exporting nations lose. As we know these trade-offs are measured in opportunity costs.
Using the same amount of resources the United States and Canada can both produce lumberjack shirts and lumberjack boots as shown in the production possibilities frontiers in the figure to the right. Comparative advantage is a key insight that trade will still occur even if one country has an absolute advantage in all products. Thus the country that faces lower.
At a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. C importing nations gain and exporting nations lose. To see the difference consider an.
The theory of comparative advantage shows that even if a country enjoys an absolute advantage in the production of goods Normal Goods Normal goods are a type of goods whose demand shows a direct relationship with a consumers income. If nations trade on the basis of comparative advantage_____ Will occur if a nation has a comparative advantage in the production of a good. For example countries with plentiful oil resources can generally produce oil inexpensively.
While the theory makes perfect sense to me and I can see why it would benefit different countries to trade together and importexport different goods to maximize profitability and production costs etc I am struggling a little to ever find real world examples. This happens for the reason that though the lower-cost country suffers by importing some goods from the higher-cost country it is more than remunerated by focused its resources on the production of those. Yes all it requires is that the comparative advantage ie.
Many countries and economies use it to determine what goods and services they plan to import or export. An important aspect that is omitted if we only look at absolute advantages is the presence of opportunity costs. This is the basis for the theory of comparative advantage.
First countries can have an advantage because they are richly endowed with a particular natural resource. The reason is the principle of comparative advantage which says that each country should specialize in the products that it can produce most readily and cheaply and trade those products for goods that foreign countries can produce most readily and cheaply. It means that the demand for normal goods trade can still be beneficial to both trading partners.
All countries only have a certain amount of resources available so they always face trade-offs between the different goods. Because Saudi Arabia produces oil very cheaply it holds a comparative advantage in oil and it exports oil in order to finance its purchases of imports. As a result Ricardo later expanded it in his book entitled On the Principles of Political Economy published in 1819 incorporating the theory of comparative advantage as the basis for why nations should trade and why trade is mutually beneficial.
Comparative advantage suggests that countries will connect in do business with one another exporting the commodities that they have a relative advantage in efficiency. They largely influence how and why nations and businesses devote resources to the. This therefore brings about relative efficiency that differentiates production of goods between the two countries Suneja 2000 p.
Trade is driven by the differences between us and the opportunity to specialize in what we do most effectively even makes the observable differences more dramatic than the underlying differences. Ricardos Comparative Advantage Doctrine. This specialization ensures greater product availability and lower prices.
Instead he concluded that trade would benefit both nations if comparative costs differ. Comparative advantage was the economic theory theorized by David Ricardo in the 19th century. The principle of comparative advantage indicates that mutually beneficial international trade can take place only when.
Comparative advantage on the other hand is the beneficial trade between countries despite one country having the upper hand of producing all of its goods by use of minimum resources. If nations trade on the basis of comparative advantage A a nation can gain only at the expense of trading partners B exporting nations gain and importing nations lose. - If one nation has the comparative advantage in one product then the other nation would have the comparative advantage in the other product.
Comparative advantage is a key principle used in international trade that forms the basis for why free trade is beneficial to all countries. A country can specialize in producing that for which it has a comparative advantage and then trade for other needed goods and services. With absolute advantage and competitive advantage Trade occurs because traders anticipate gains from trading Comparative advantage determines why nations regions and individuals trade The basis for trade is differing opportunity costs among nations Nations regions individuals specialize in producing.
If nations trade on the basis of comparative advantage. A B increase the.

Solved 47 If Nations Trade On The Basis Of Comparative Chegg Com
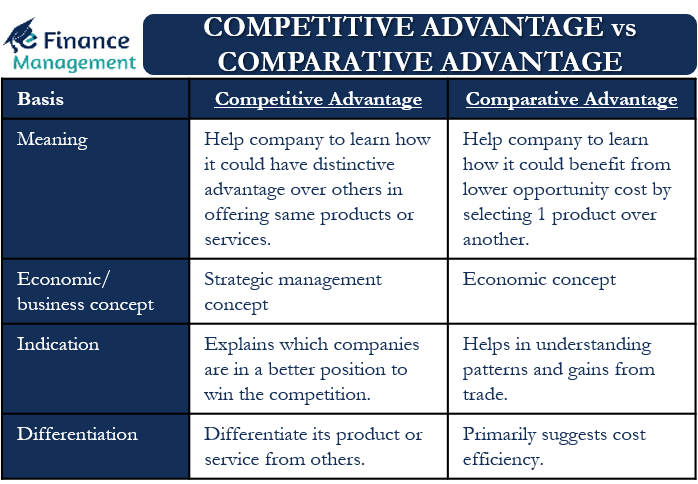
Competitive Advantage Vs Comparative Advantage All You Need To Know

Example Of Comparative Advantage From A Table Of Data Video Khan Academy
Comments
Post a Comment